Cadmium Toxicity
Short term and long term exposure to cadmium is animals and humans
may cause high blood pressure,
anemia and kidney effects.
 Cadmium is found in very concentrations in most rocks, coal and petroleum (oil) products
and often in combination with zinc. It is introduced into the environment from mining and smelting operations.
Other cadmium emissions are from fossil fuel use, fertilizer application, sewage sludge disposal or galvanized
pipe corrosion. Cadmium is found in very concentrations in most rocks, coal and petroleum (oil) products
and often in combination with zinc. It is introduced into the environment from mining and smelting operations.
Other cadmium emissions are from fossil fuel use, fertilizer application, sewage sludge disposal or galvanized
pipe corrosion.
Sources of Cadmium Toxicity[3]
 ENVIRONMENTAL/OCCUPATIONAL SOURCES OF CADMIUM TOXICITY ENVIRONMENTAL/OCCUPATIONAL SOURCES OF CADMIUM TOXICITY
• Tobacco smoke
• Phosphate fertilizers
• Fossil fuel combustion
• Cement production
• Incineration of municipal waste
• By-products from zinc, lead, or copper ore smelting
• Battery manufacturing
• Plastic manufacturing
HOUSEHOLD SOURCES OF CADMIUM TOXICITY
• Contaminated vegetables
• Cosmetic pigments (red and yellow)
• Teflon in cooking pans
• Children’s toys
• Paints
• NiCad batteries
• Food (shellfish, liver and kidney meats)
• Tattoos
MEDICAL SOURCES OF CADMIUM TOXICITY
• Dental restorations
• Amalgams and dental root
fillings
Additional Cadmium Toxicity Sources Include:
Shellfish, liver and kidney meats, soft
water, tobacco. Mining and smelting processes (e.g. Lead and zinc). Nickel-cadmium batteries, PVC plastics,
paint pigments. Insecticides, fungicides, sludge, and commercial fertilizers. Other sources include; dental
alloys, electroplating, motor oil, and exhaust.
Synergistic for Cadmium
Toxicity Uptake/Retention in the Body:
Iron deficiency. Lead and mercury
accentuate toxicity.
Antagonistic for Cadmium Toxicity Uptake/Retention in the Body:
Adequate zinc, calcium, magnesium, and
copper
Cadmium Toxicity Physiological Interactions in the Body:
Kidney proximal tubule is main site of
accumulation. May modify catecholamine metabolism. Decreases CYP-450. Inhibits antitrypsin. Changes in arterial
endothelium seen.
Symptoms of Excessive Cadmium Toxicity Exposure:
Low blood pressure, high blood pressure, fatigue,
anemia, protein in the urine, osteomalacia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, emphysema. Cadmium target organs are the
liver, placenta, kidneys, lungs, brain, and bones.
Assess, don't
guess!
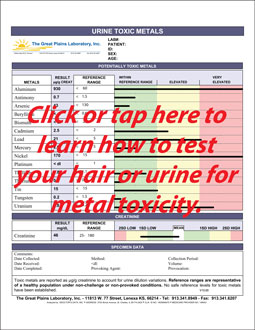
How to test your body for Cadmium
Toxicity:
Heavy Metal Screening Test (this is an inexpensive screening)
Hair Metal Toxicity Test
Urine Heavy Metal Test
How to test water for Cadmium
Toxicity: WaterCheck
Recommended cadmium water treatment: Distillation or Reverse Osmosis[1]
This is not an all-encompassing list. There are
other sources of metal exposure not listed herein.
This is not an all-encompassing metal
toxicity list. There are other sources of metal exposure not listed herein.
References
[1] National
Testing Laboratories, Ltd. Corrective Action Brochure
[2] Genova Diagnostics
Toxic & Nutrient Elements Chart[3] NeuroScience Melissa Test and "Hidden Sources of Metal Exposure"
Return from Cadmium Toxicity to Water Quality and Toxicities
|