Information, Tests and Solutions to Improve
Your Health and Water Quality |
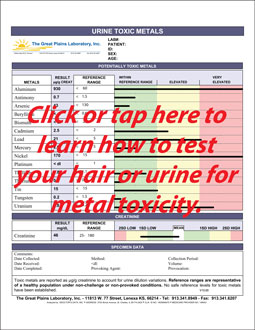
Gallium ToxicityGallium Toxicity Symtoms, Sources and Treatments
|
You are here: Home Page > Heavy Metal Toxicity > Gallium Toxicity
Natural Care Solution:
Helping People Improve Their Health Naturally Since
1998
|
Quality Water Testing and Analysis for Residential and Commercial Water Sources
My Mission
Provide you with accurate information, economical and
effective tests
and products to evaluate your body and water for toxic metals and remove them if
necessary.
Keith D. Bishop
Clinical Nutritionist
B.Sc. Pharmacy
Health
Coach©

|
*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products are
not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease.
The information and contents of this website are based upon government, medical,
university and health industry research information.
Consult with your physician or a qualified health care provider before making any changes in your medical or
treatment program.
Please let us know if you have problems viewing anything or ordering on this page:
Thank you for visiting www.ToxicWaterSolution.com! If you find this information helpful or
interesting please send a link to your family and friends.
Copyright © 2007-2016 Natural Care Solution, LLC Keith D. Bishop, Clinical Nutritionist, B.Sc. Pharmacy